Ergothionein
Functional research
Multiple confirmed immunomodulatory effects:
Improve sleep quality
Enhance memory
Anti hyperglycemic induced endothelial injury
Anti skin photoaging
1、Improve sleep quality
Human clinical practice: Consuming 20 milligrams of BIO-EGT daily for 4 weeks can significantly improve sleep quality.
(Makoto Katsube .(2022);Food-derived antioxidant ergothioneine improves sleep difficulties in humans)
Experimental design: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial was conducted with 429 volunteers (aged 40 to 75) suffering from anxiety and sleep problems.After excluding samples that did not meet the inclusion criteria, a total of 100 people were enrolled in the study using Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), Athens Insomnia Scale (AIS),State Trait Anxiety Scale (STAI) questionnaire, and Sleep Efficiency (EEG) score. The participants were randomly divided into a ergotamine group and a placebo group.The subjects took 20mg ergotamine or placebo daily for 4 weeks.
Result: Ergothionein can significantly improve sleep difficulties, increase non rapid eye movement sleep, reduce the latency period to falling asleep and the frequency of waking up after falling asleep.
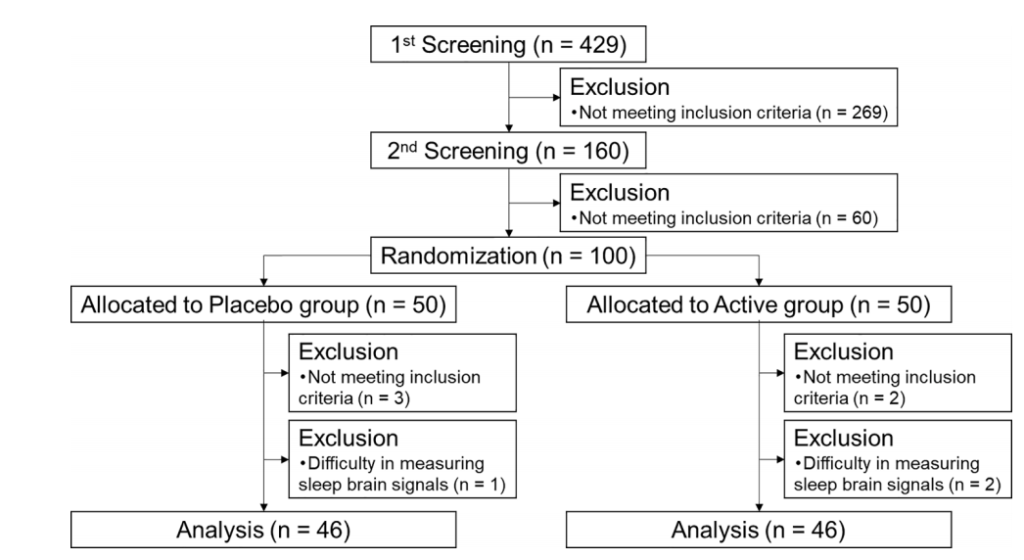
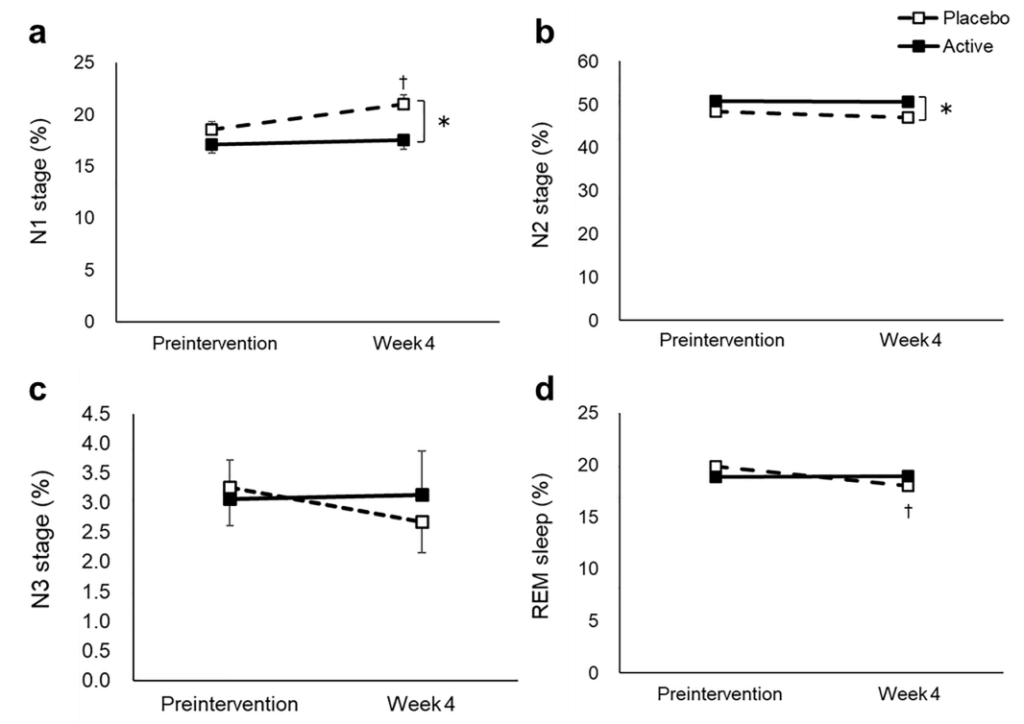
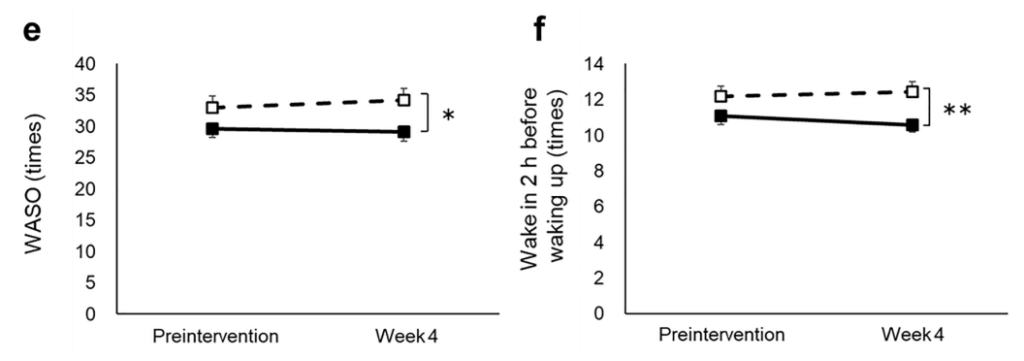
a N1 stage, b N2 stage, c N3 stage, d REM stage, e WASO, f wake in 2 h before waking up, g SWS latency, h sleep efficiency, i delta power during the first sleep cycle, and j total sleep time were measured before and after the intervention. The dotted and solid lines indicate the placebo (n = 46) and active group (n = 46), respectively. Mean values with standard error of the mean; **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 (Welch t-test); † P < 0.05 versus baseline (paired t-test). EEG, electroencephalograph; SWS, slow wave sleep; REM, rapid eye movement; WASO, wake after sleep onset.
2、Enhance memory
Animal efficacy experiment: ICR mice orally administered ergotamine (dose of 1-50 mg/kg) showed significantly higher discrimination indices in both new object recognition and spatial recognition tests compared to the control group.
(Noritaka Nakamichi.(2021);Oral Administration of the Food-Derived Hydrophilic Antioxidant Ergothioneine Enhances Object Recognition Memory in Mice)。
Experimental design: ICR mice were orally administered ERGO (doses ranging from 1-50 mg/kg) three times a week for two consecutive weeks; We used new target recognition experiments, spatial recognition experiments, LC-MS/MS, Golgi staining, neuron culture, western blotting, immunohistochemistry, RT-PCR and other methods to study the enhancing effect of oral ergotamine on object recognition memory in normal mice.
Result: Oral administration of ergotamine can enhance the ability to recognize and remember objects, and this enhancement effect is achieved by promoting the maturation of hippocampal neurons.
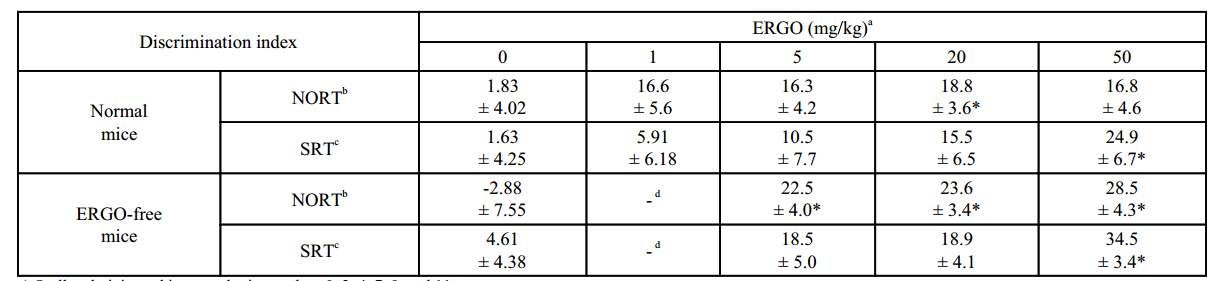
a) Orally administered in normal mice on days 0, 2, 4, 7, 9, and 11
b) Performed at three days after the last ERGO administration
c) Performed at six days after the last ERGO administration
d) Not performed
* Significant difference from the corresponding control values (P < 0.05)
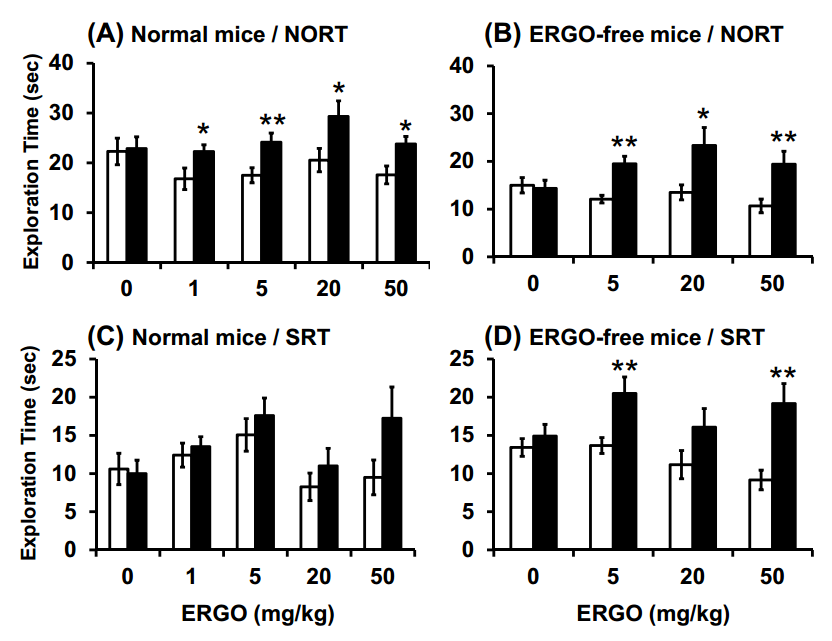
Fig. (1). Effect of oral administration of ERGO on object recognition and object location memory under normal conditions.
Normal (A, C) and ERGO-free (B, D) mice were orally administered ERGO at 0, 1, 5, 20, or 50 mg/kg on days 0, 2, 4, 7, 9, and 11. Three and six days after the final ERGO administration, NORT (A, B) and SRT (C, D) were conducted, respectively, and the exploration time was measured. The white and black columns in panels (A) and (B) display the exploration time for the familiar and novel objects, respectively.
The white and black columns in panels (C) and (D) show the exploration time for the unmoved and moved objects, respectively. Each value represents the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 12–15). * Significant difference from the control (P < 0.05); ** Significant difference from the control (P < 0.01).
3、Effectively protect endothelial cell aging induced by hyperglycemia
Cell experiment: ergothione can interfere with the aging of endothelial cells related to hyperglycemia by regulating SIRT1 and SIRT6 signal transduction, protect the oxidative damage induced by hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
(Nunzia D’Onofrio.(2016); Ergothioneine oxidation in the protection against high-glucose induced endothelial senescence: Involvement of SIRT1 and SIRT6)
Experimental design: Endothelial cells were incubated in a gradient concentration of ergothionein solution (0.01-1.00 mM) for 12 hours, followed by incubation in high glucose (25 mM) for 48 hours. Cell evaluation shows that a concentration of 0.5 mM ergotamine can effectively prevent high glucose induced cytotoxicity.
Conclusion: Ergothionein can resist the aging of endothelial cells induced by high blood sugar and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
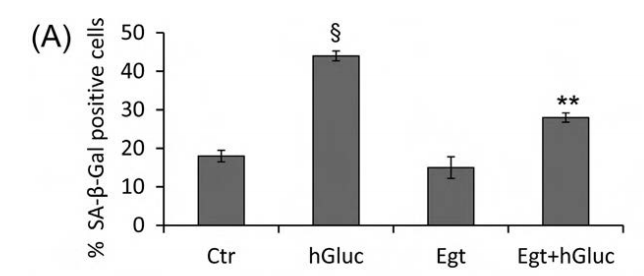
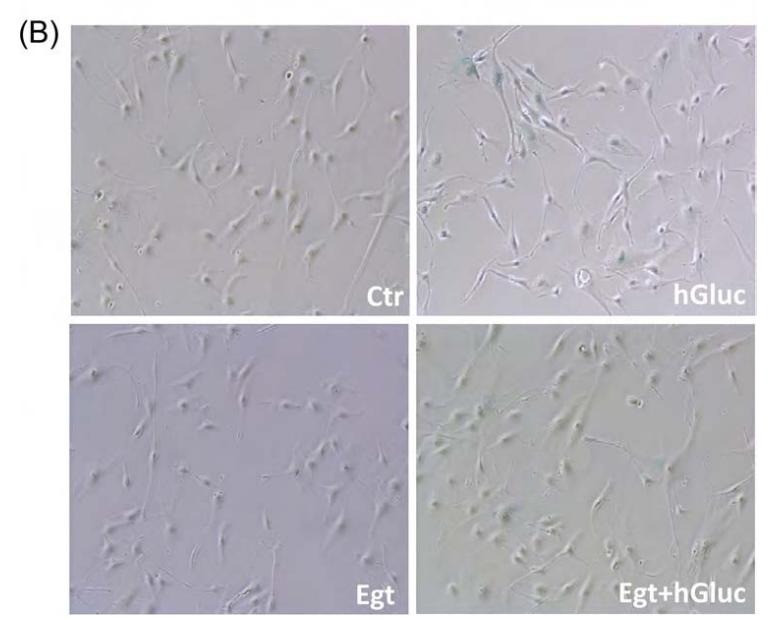
Fig. 3. Effect of ergothioneine on high-glucose induced EC senescence. (A) Percentage of SA-β-galactosidase staining positive EC grown for 48 h with high-glucose (hGluc), high-glucose plus ergothioneine (0.5 mM) (EgtþhGluc), ergothioneine (Egt) (0.5 mM), or media containing nGluc (Ctr). (B) Representative images of SA-β-galactosidase staining (blue). Data are the mean7SD of five independent experiments with **Po0.01 vs. hGluc and § Po0.01 vs. Ctr.
4、Ergothionein has anti skin photoaging properties
Cell experiment: Ergothionein alleviates skin fibroblast aging caused by UVB damage by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and HSP70 in keratinocytes.
(Hyun Ju Ko.(2021);Ergothioneine alleviates senescence of fibroblasts induced by UVB damage of keratinocytes via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and HSP70 in keratinocytes)
Experimental design: Keratinocytes were pretreated with ergothionein and then irradiated with UVB to evaluate ROS production and apoptosis. The Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, HSP70, pro apoptotic proteins, and paracrine cytokines were also analyzed by Western blotting and real-time PCR. Collagen degradation related genes and aging were also evaluated.
Result: Pre treatment of keratinocytes with ergothionein significantly inhibited the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and downregulation of HSP70, and protected keratinocytes by inhibiting ROS production and cleavage of pro apoptotic proteins (including caspase-8 and PARP). In addition, ergotamine significantly reduces paracrine cytokines, including IL-1 β, IL-6, and TNF – α. In fibroblasts co cultured with keratinocytes treated with ergotamine, the expression levels of collagen degradation related genes and fibroblast aging were significantly reduced; The synthesis of type I procollagen significantly increased.
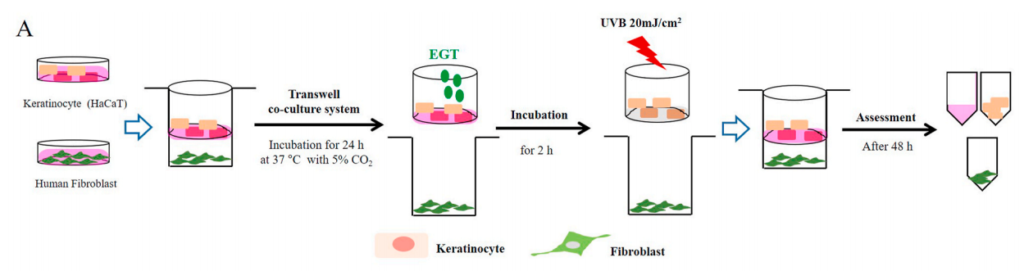
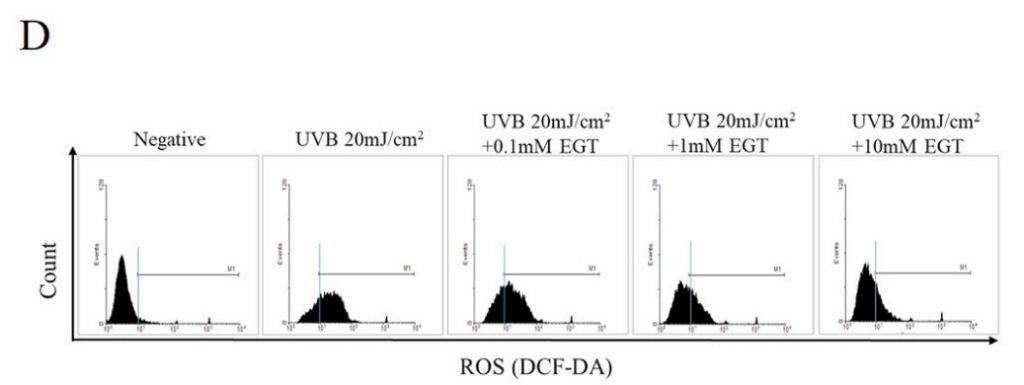
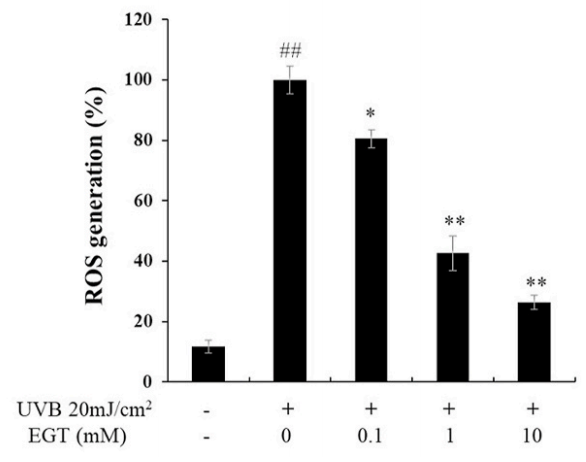
Fig. 1. Effects of ergothioneine (EGT) on keratinocyte viability and oxidative stress in keratinocytes following ultraviolet B (UVB) exposure using a co-culture system containing keratinocytes and fibroblasts.
(A) Keratinocytes in the upper chamber and fibroblasts in the lower chamber were incubated for 24 h at 37 ◦C under 5% (v/ v) CO2. Keratinocytes with or without EGT pretreatment for 2 h were stimulated with UVB (20 mJ/cm2 ). Stimulated keratinocytes with or without EGT were cocultured with fibroblasts. After 48 h, the culture media and cells were harvested.
D) UVB-induced intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in keratinocytes.
EGT inhibited ROS synthesis in keratinocytes following UVB irradiation. #p < 0.05 vs. negative control; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. vehicle-treated keratinocytes.
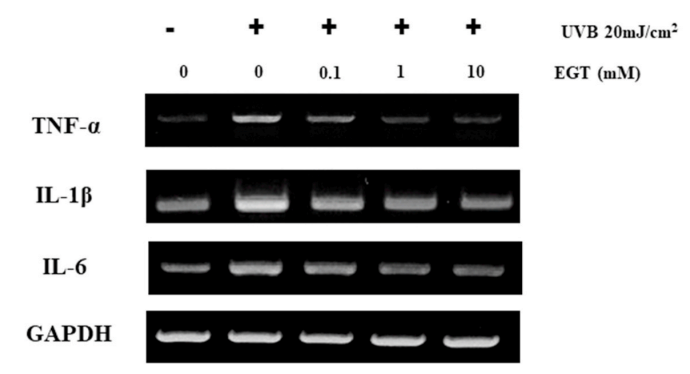
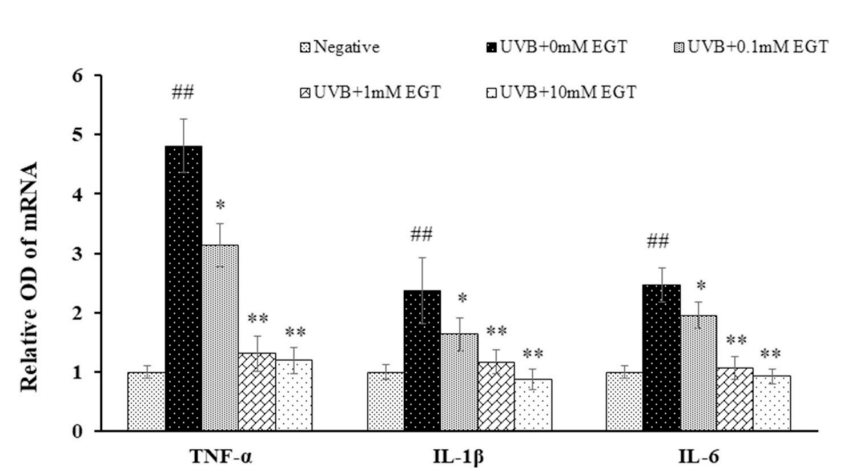
Fig. 5. EGT-mediated suppression of UVB-induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in keratinocytes. The mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) in UVB-irradiated keratinocytes with and without EGT treatment were examined by RT-PCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Quantification of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression following normalization to GAPDH. #p < 0.05 vs. negative control; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs.vehicle-treated keratinocytes.
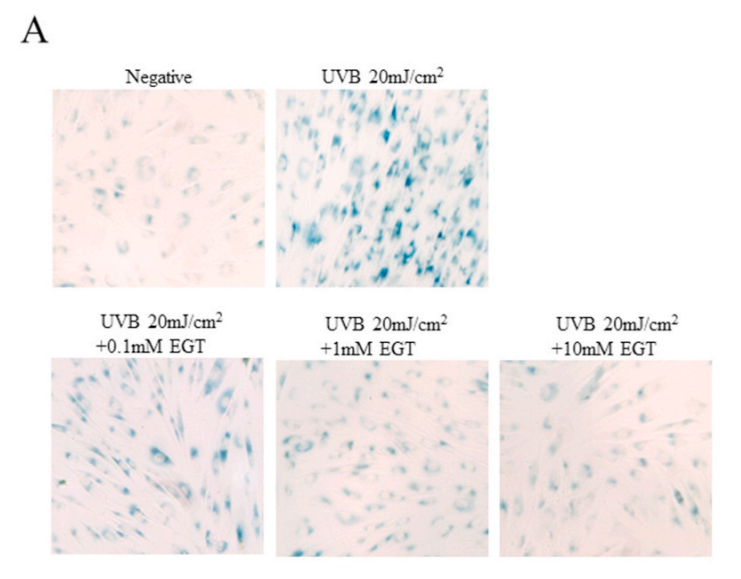
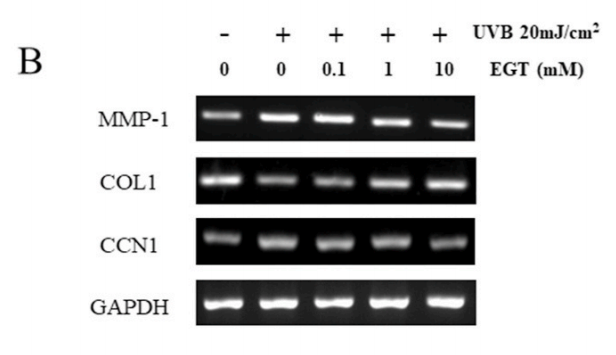
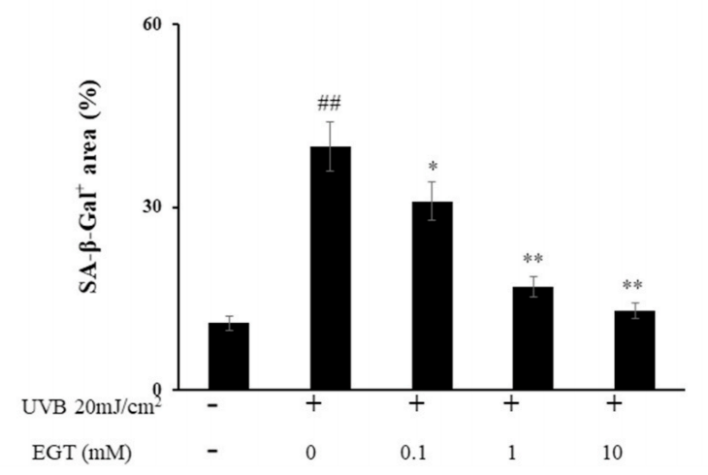
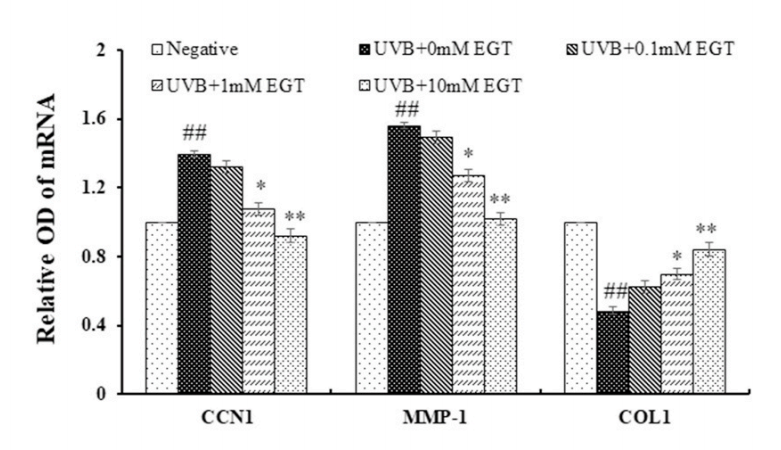
Fig. 6. Effect of EGT pretreatment of keratinocytes on UVB-induced photoaging in fibroblasts. (A) Fibroblasts were assessed by SA-β-gal staining. Quantitative analyses of senescent cells are indicated by the percentage of positive staining compared to the vehicle-treated group. (B) mRNA levels of collagen homeostasisassociated proteins (MMP-1, COL1, and CCN1) were quantified by RT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH as an internal control. ##p < 0.01 vs. negative control; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. fibroblasts with vehicle-treated keratinocytes.
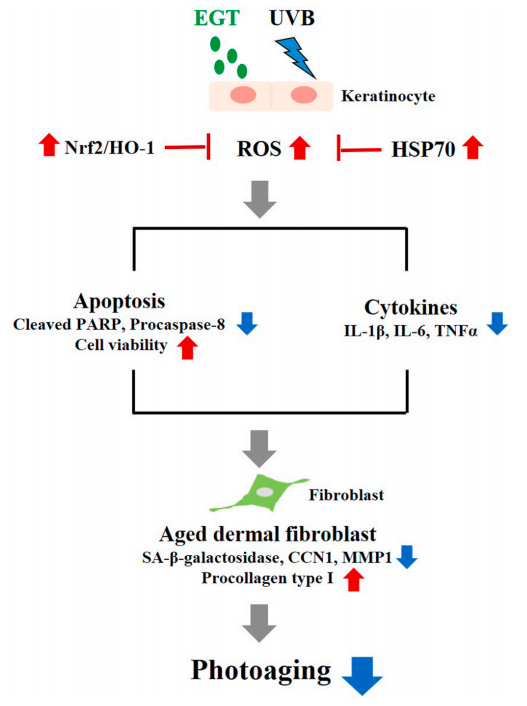
Fig. 7. Schematic illustration of the anti-photoaging effects of EGT in a keratinocyte/fibroblast co-culture system following UVB irradiation. UVB-irradiated keratinocytes promoted ROS synthesis, apoptosis, and production of proinflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, fibroblasts co-cultured with UVBirradiated keratinocytes showed changes in MMP-1, CCN1, and procollagen type I. The anti-photoaging effects of EGT in UVB-irradiated skin damage was mediated by suppression of the upregulation of ROS, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and keratinocyte apoptosis, and by maintaining collagen homeostasis in fibroblasts. CCN1, cysteine-rich protein 61; EGT, ergothioneine; HSP, heat shock protein; IL, interleukin; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; UVB, ultraviolet B.
